Industrial air-cooled chillers are an essential component in many industrial processes, providing the necessary cooling to maintain optimal operating conditions for machinery. These chillers, as the name suggests, rely on air to dissipate heat from the system, making them a popular choice for many applications where water access might be limited or restricted.
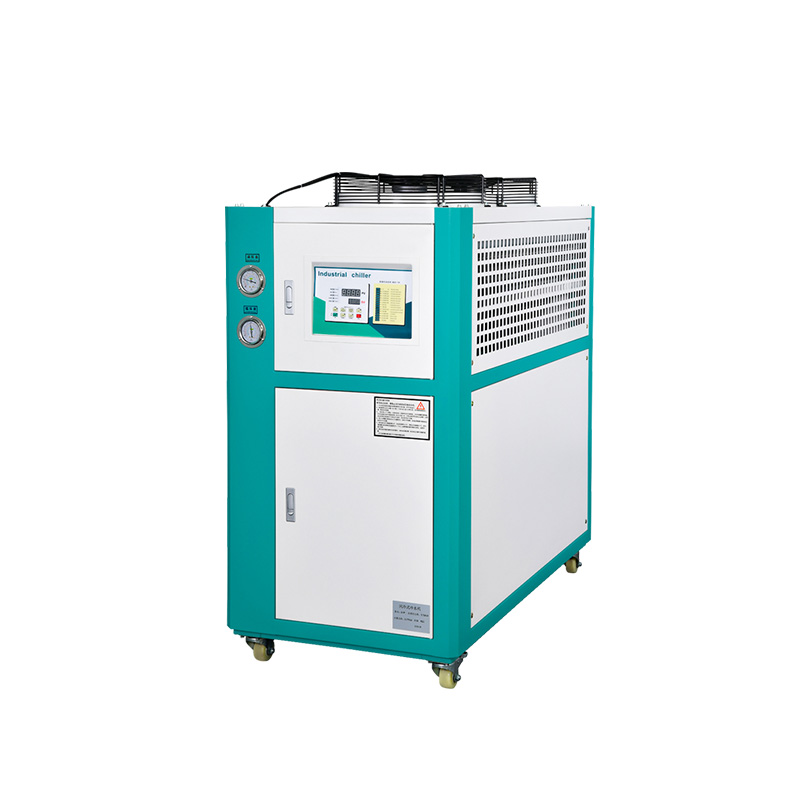

An industrial air-cooled chiller is a refrigeration system designed to cool fluids through the absorption or steam compression cycles. The fundamental components that make up these systems include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve.
Compressor: The compressor’s main function is to compress refrigerant, converting it into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas.
Condenser: Once the refrigerant is compressed, it passes through the condenser, where it is cooled and turned back into a liquid state by dissipating heat into the surrounding air.
Expansion Valve: The expansion valve reduces the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it for the cooling process in the evaporator.
Evaporator: In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the circulating water or other fluid that requires cooling, and this heat absorption results in the cooling of the fluid, which can then be circulated through the industrial machinery or equipment.
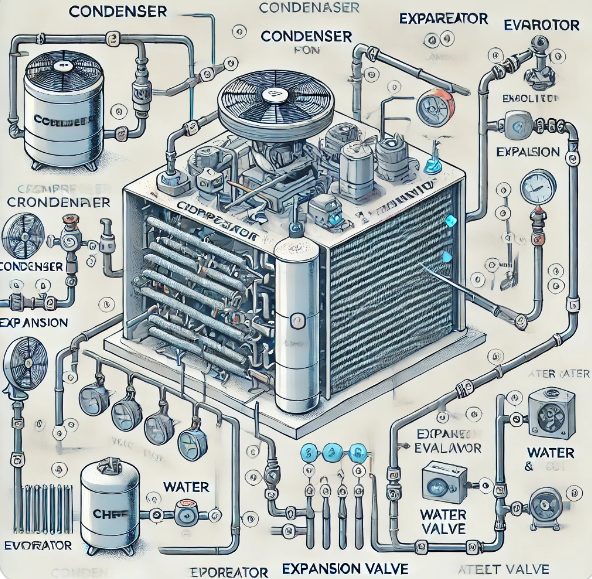
The distinguishing feature of an air-cooled chiller compared to its water-cooled counterpart is the method used for heat dissipation. Instead of relying on water and cooling towers, air-cooled chillers use fans to expel the heat into the atmosphere, making them ideal for locations where water supply may be scarce.
Air-cooled chillers offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications:
Ease of installation: Since they do not require additional equipment such as cooling towers or complex plumbing systems, air-cooled chillers are relatively easier to install compared to water-cooled chillers.
Lower maintenance requirements: With fewer components involved in the cooling process, air-cooled systems typically demand less maintenance than their water-cooled counterparts, particularly in environments where water quality is an issue.
Cost-effectiveness: The absence of water consumption makes air-cooled chillers more economical, particularly in areas where water costs are high or where water conservation is a priority.
Mobility: Air-cooled chillers are often used in temporary setups due to their portability, providing cooling solutions in facilities that may change location or where permanent systems are unnecessary.
These advantages, combined with the robust cooling capabilities, make air-cooled chiller systems a popular choice for industries such as plastics, laser technology, food processing, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning).
While both air-cooled and water-cooled chillers are effective at cooling, the specific application and environmental factors can determine which system is better suited for a given situation. Below are some points of comparison:
Cooling Efficiency: Water-cooled chillers typically offer better cooling efficiency than air-cooled chillers, especially in hot climates. However, air-cooled chiller units are more suitable for environments where water conservation is important.
Operating Environment: Air-cooled chillers can operate in areas where water is either unavailable or not viable due to cost or location restrictions. On the other hand, water-cooled chillers require a reliable water source, making them better for environments where ambient temperatures are consistently high.
Installation and Setup: Air-cooled chillers do not require the extensive setup of a cooling tower system, which can reduce upfront installation costs and complexity. Water-cooled systems are typically more suited for large, permanent installations where long-term efficiency is a priority.
In situations where cooling needs are critical but water resources are scarce, industrial air-cooled chiller systems offer a viable solution without compromising performance.
Industrial air-cooled chillers are used across a wide range of industries. Some notable examples include:
Plastics Industry: Air-cooled chillers provide cooling for injection molding machines, ensuring optimal mold temperature control and reducing production cycle times.
HVAC Systems: In commercial and industrial HVAC setups, air-cooled chillers help regulate the temperature of large buildings, maintaining a comfortable environment for occupants.
Food and Beverage Industry: These chillers play a critical role in food processing and storage by maintaining the right temperature for sensitive ingredients and finished products.
Laser Equipment: Lasers generate a significant amount of heat during operation, and air-cooled chillers provide the cooling necessary to maintain laser efficiency and prevent overheating.
By offering reliable and consistent cooling, air-cooled chillers contribute to enhanced productivity and product quality across these and many other industrial applications.
When selecting an industrial air-cooled chiller, several factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency:
Cooling Capacity: The cooling load requirements of your specific application will determine the size and capacity of the chiller you need. A 5HP chiller, for example, may be suitable for smaller-scale operations, while larger industrial processes might require more powerful units.
Operating Environment: Ambient temperature and environmental conditions can impact the efficiency of air-cooled chillers. It's important to select a chiller that can operate effectively within your temperature range.
Energy Efficiency: Look for chillers with energy-saving features, as these will not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to a smaller carbon footprint.
Maintenance Requirements: Consider the long-term maintenance demands of the chiller system. Air-cooled chillers typically have lower maintenance needs, but it's still essential to ensure regular servicing to maximize lifespan and efficiency.
In summary, industrial air-cooled chillers are an efficient, cost-effective, and versatile cooling solution for many industries. Their ability to operate without relying on water makes them particularly well-suited for environments with limited water resources, and their ease of installation and maintenance make them a practical choice for a range of applications. By understanding the basics of air-cooled chillers, including their operation, benefits, and applications, you can make informed decisions when choosing the right chiller system for your industrial cooling needs.
Whether it's cooling injection molding machines, laser equipment, or maintaining optimal temperature in food processing, air-cooled chillers continue to play a crucial role in modern industrial processes.Qindao Machinery has been committed to industrial chillers for more than 20 years. We provide the most professional and high-quality services. If you need industrial chillers/refrigeration machines, please contact us at 2314609053@qq.com and we will contact you within 24 hours.